Ferrets can eat a variety of foods like fruits, vegetables, and meat. But carbohydrates and vegetables don’t complete the needs of the nutrition of ferrets. It makes their health and body poor.
So ferret’s primary diet should rely on animal meat protein. Even feeding your ferret a diet of raw food can provide numerous health benefits and help keep them in top shape. So here you will get the complete guide about raw food for ferrets.
Basic Ferret Feeding Rules
Ferrets are obligate carnivores, and their rapid digestive system necessitates a diet rich in animal proteins, high in fat, and low in fiber. While ferrets have a penchant for sweet treats, it’s imperative to resist the temptation, steering clear of sugary indulgences like raisins and fruits.
When choosing commercial ferret diets, the key lies in prioritizing meat, poultry, fishmeal, or animal by-products as the primary ingredients. Despite their love for fruits and veggies, ferrets struggle to digest fiber efficiently.
The caveat here is that while experts caution against excess fiber, it doesn’t mean avoiding it entirely. Ferrets do need nutrients typically obtained from animal-based meals.
The most suitable ferret diet is whole prey or a balanced fresh one, practicality often leads to unique regimens. Experts recommend pelleted diets with 30 to 35 percent meat-based protein and 20 percent animal fat.
For those easing into raw feeding, commercially packaged food with 30 to 35 percent crude protein and 15 to 20 percent fat is a good start, as long as it’s based on high-quality meat, not grains.
Raw Food For Ferrets

A balanced raw diet for your ferret means a meticulous blend of meat, bones, and organs. The ratio will be 80% meat, 10% bones, and 10% organs, similar to the proportions of a whole animal: 80% flesh, 10% skeleton, and 10% internal organs.
This rule is a practical guide so that your ferret gets a well-rounded nutritional profile. While feeding them whole prey is the most natural way to maintain this balance, it can pose difficulties with non-imprinted ferrets who might be resistant to such meals.
Ferrets rely on their food by six months old, but making the switch to raw feeding is a patient process for those not initially weaned on it. They thrive on a diet centered around meat. The best option is raw meat, encompassing whole prey for a wholesome nutritional profile.
When it comes to raw meat, ferrets can savor a variety, including chicken wings and stripped carcasses, turkey necks, rabbit, game birds, pigeons, minced beef, lamb, offal, lamb’s heart, and raw animal bones which is essential calcium and dental hygiene. Raw chicken and lamb stand out as particularly favored choices.
Whole prey is another exciting option for ferrets, encompassing mice, rats, and chicks. This aligns with their instincts and offers a diverse nutritional profile.
Additionally, ferrets can indulge in kitten food, which boasts a high meat protein content, baby food rich in meat protein, and dried ferret food designed to meet their carnivorous cravings.
For a delightful occasional treat, eggs are a welcomed addition to your ferret’s menu. However, it’s crucial to maintain a balanced diet, ensuring that 32-38% of the intake is protein, and 15-20% is fat. This balance contributes to their overall well-being and vitality.
Pros and Cons of Feeding Raw Food to Ferrets
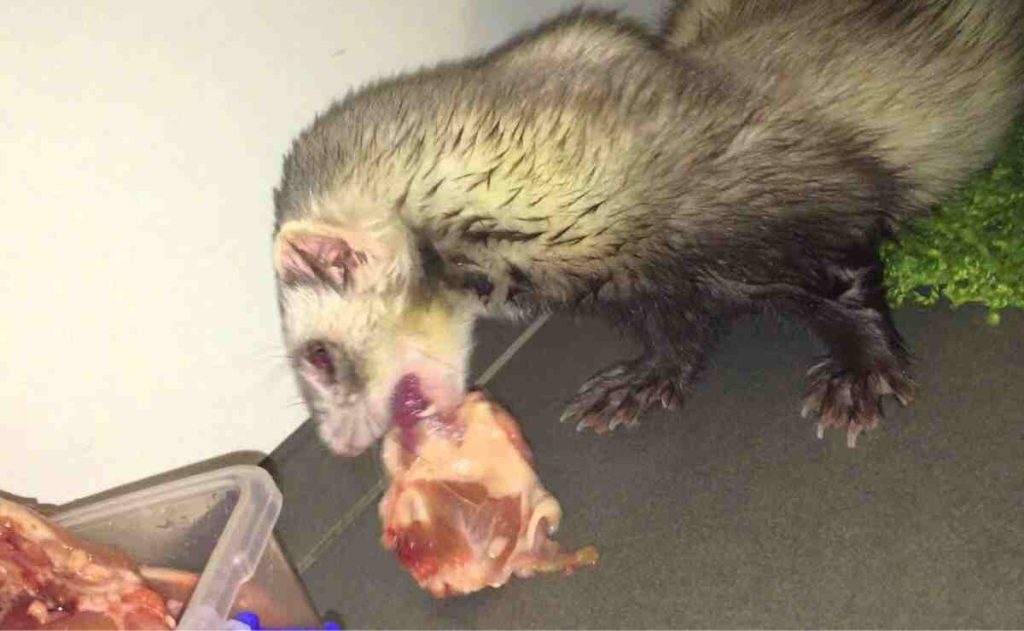

Raw diets for ferrets have gained popularity as it is a natural and biologically fitting approach to nourishing your furry companions. Whether opting for commercial brands or preparing gourmet meals at home, a raw feeding routine requires dedication and understanding.
Pros of Feeding Ferrets Raw Foods
1. Natural Health Boost: Fresh food rich in animal protein, fat, and essential nutrients helps to maintain your ferret’s health as naturally as possible.
2. No Artificial Additives: Choosing freshly cut meats over commercially manufactured dry foods eliminates concerns about artificial flavorings or additives.
3. Dental Health: Feeding edible bones helps prevent tartar buildup on ferrets’ teeth and adds essential calcium to their diet.
4. Improved Coat Condition: Many ferret owners observe enhanced coat conditions, characterized by increased shine and softness, along with a reduction in stool volume.
5. Enrichment: Raw feeding diets that incorporate whole prey fulfill ferrets’ natural hunting instincts, providing mental and physical enrichment.
Cons of Feeding Ferrets Raw Foods
1. Challenge in Proportion Sizes: Maintaining proper proportion sizes and meal frequency can be challenging, as ferrets’ diets vary based on factors such as time of year, sex, age, and weight.
2. Fluctuating Diets: Ferrets’ diets fluctuate, posing difficulties in establishing a consistent feeding regimen.
3. Nutrient Imbalances: Some grinds offer incomplete or imbalanced nutrient profiles, potentially requiring additional supplements, meat, and organs, making the diet more expensive.
Despite the challenges, feeding a raw diet can be a healthy option for your ferret. The effort invested in understanding and maintaining the feeding routine pays off with a nutrient-rich diet that addresses hygienic concerns and supports your ferret’s overall well-being.
It may be a labor-intensive journey, but the benefits, from improved health to dental care, make it well worth the effort once you establish a consistent and effective routine.
How Much To Feed Raw Food to Your Ferrets?
A ferret’s proper dietary needs are essential but it depends on various factors like age and especially season playing significant roles. Young ferrets under one year old can easily consume 10% or more of their body weight daily, equating to 100g per 1kg of weight. This robust appetite is crucial for their rapid growth and development.
As seasons transition, the dietary requirements of ferrets undergo noticeable changes. Adult ferrets gearing up for winter may also consume around 10% of their body weight, bulking up to prepare for the colder months and develop a thicker winter coat.
In contrast, during the summer, an adult ferret is likely to eat only about 3% of their body weight, resulting in a slimmer physique with a shorter coat.
Feeding amounts fluctuate significantly throughout the year, making it challenging to provide a set amount to feed. As a rough guideline, ferrets generally consume approximately 60-80g in late summer. This intake can increase to 100-140g in autumn as they prepare for winter.
During the winter months, the amount may drop back to around 80g. It creates a balance between energy conservation and nutritional needs. The lead-up to spring sees another decrease, with some meals as small as 50g during the shedding of winter coat and fat.
When selecting meat types for your ferret, it’s essential to incorporate at least three different protein sources to ensure a balanced nutritional profile. Poultry or game birds, red meat, pork, and fish are common choices among ferret owners.
Commonly fed whole prey items include rodents (mice, rats, guinea pigs), rabbits, birds (chicken, quail), and even reptiles and amphibians (frogs, lizards). These items provide a diverse range of nutrients and fulfill your ferret’s instinctual drives.
What do ferrets eat in the wild?
In the wild, ferrets are true carnivores, and their diet includes every part of the animal like meat and bones. This natural eating behavior not only contributes to their overall health but also provides valuable stimulation and exercise for their jaws.
If you understand the wild life dietary habits of ferrets, then you have a good insight into how to replicate these conditions in a domestic setting. Sadly, not all ferrets receive optimal care. Many domestic ferrets face severe health issues due to insufficient nutrients.
As a result, they are unable to walk and a significant portion of their body weight lose in just a few weeks. So you should give importance to proper care and nutrition for these wonderful creatures.
Is Commercial Food Good For Ferrets?
Many ferret owners opt for commercial ferret food, but there is a growing trend towards feeding ferrets a raw diet, which is believed to mimic their natural diet in the wild more closely.
A raw food diet for ferrets typically consists of whole prey animals, such as mice or small birds, as well as other raw meats and organs. This type of diet provides ferrets with the essential nutrients they need to thrive, including high-quality proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of vitamins and minerals.
When preparing a raw food diet for your ferret, it is important to ensure that the ingredients are fresh and of high quality. Look for locally sourced meats and organs that are fit for human consumption. It is also crucial to include a balance of different protein sources, such as chicken, rabbit, and turkey, as well as some organ meats to provide essential nutrients.
It is important to note that a raw food diet for ferrets may not be suitable for every pet. Some ferrets have specific dietary requirements or health conditions that may require a different type of diet. As always, it is best to consult with your veterinarian before making any changes to your ferret’s diet.
Conclusion
Feeding your ferret a raw food diet can offer a range of benefits like improving digestion, healthier skin and coat, increased energy levels, and a stronger immune system. It is essential to introduce the diet slowly and monitor your ferret’s health and well-being closely.
A raw food diet can be a fantastic option for ferret owners looking to provide their pets with a natural and nutritious diet. However, it is essential to do thorough research and consult with a veterinarian to ensure it is the right choice for your ferret.
